Industries worldwide are increasingly concerned with reducing harmful emissions, particularly nitrogen oxides (NOx), due to their severe environmental and health impacts. NOx emissions contribute to smog, acid rain, and respiratory problems, making effective control measures essential. One of the most efficient technologies for mitigating NOx pollution is the NOx wet scrubber. These devices use a liquid medium to absorb and neutralize NOx from industrial exhaust streams, converting them into harmless substances. This blog post delves into the mechanisms, designs, and benefits of NOx wet scrubbers, providing a comprehensive guide for industrial applications.
Table of Contents
Introduction to NOx and Its Dangers
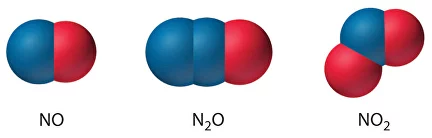
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a group of highly reactive gases that are major pollutants in industrial emissions. The most common and concerning NOx compounds include nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). These gases contribute to various environmental and health problems:
- Environmental Impact: NOx gases contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and fine particulate matter, which can lead to smog and acid rain. Acid rain, in turn, can damage forests, soils, and water bodies, disrupting ecosystems.
- Health Risks: Prolonged exposure to NOx can cause respiratory issues, aggravate existing heart diseases, and reduce lung function, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly.
Given the significant impact of NOx, effective control measures are crucial. One of the most effective technologies for controlling NOx emissions from industrial sources is the NOx wet scrubber.
Wet Scrubber Mechanism
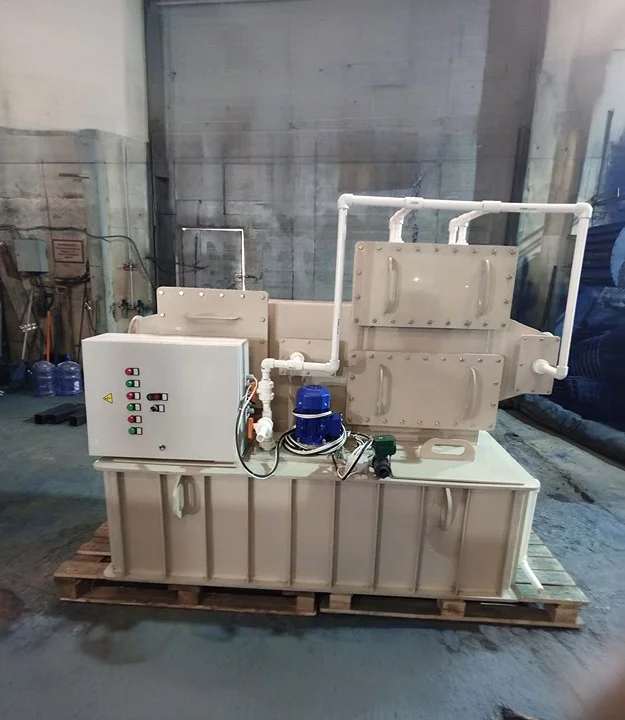

Wet scrubbers are air pollution control devices that use liquid to remove pollutants from a gas stream. In the context of NOx removal, the process involves:
- Gas Absorption: Contaminated gas is introduced into the scrubber, where it passes through a tower filled with a scrubbing solution. The solution typically contains chemicals that react with NOx.
- Chemical Reaction: Common scrubbing solutions include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and other neutralizing agents. These solutions react with NOx to form harmless compounds, such as sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
- Clean Gas Release: The purified gas, now free of NOx, is released from the top of the scrubber, while the scrubbing solution is either recirculated or treated for disposal.
Design and Efficiency
The design of a NOx wet scrubber is crucial to its efficiency. Key elements include:
- Packing Material: This material, often made of ceramic or plastic, provides a large surface area for gas and liquid contact, enhancing the absorption process.
- Scrubbing Solution: The type and concentration of the scrubbing solution are tailored to the specific NOx concentration and the desired removal efficiency.
- Flow Rate and Temperature: Both the gas and liquid flow rates, as well as the temperature, significantly impact the scrubber’s performance. Optimal conditions ensure maximum NOx absorption and chemical reaction.
Efficiency of NOx scrubbers can reach up to 99.9% under optimal conditions, making them highly effective for industrial applications.
Types of Scrubbers
There are several types of wet scrubbers, each suited to different applications and space constraints:
- Vertical Scrubbers: These are the most common type, providing high-efficiency purification. They are ideal for large industrial facilities with substantial space.
- Horizontal Scrubbers: These are more compact and easier to maintain, suitable for smaller installations or retrofits where vertical space is limited.
- Venturi Scrubbers: Utilizing a Venturi tube, these scrubbers enhance the contact between the gas and the scrubbing solution, increasing the mass transfer efficiency.
Each type has its advantages and is selected based on specific industrial requirements and space availability.
Chemicals Used in NOx Scrubbers
Different chemicals can be used in NOx scrubbers, each with its specific reactions and benefits:
- Ammonia (NH3): Often used in selective catalytic reduction (SCR) processes, ammonia reacts with NOx to form nitrogen and water.
- Urea (NH2CONH2): Another agent used in SCR, urea decomposes to form ammonia, which then reacts with NOx.
- Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3): A mild alkaline solution that reacts with NOx to form sodium nitrate and nitrite.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): A strong alkaline solution that efficiently neutralizes NOx to form non-toxic salts.
The choice of chemical depends on the specific requirements of the industrial process, including the concentration of NOx and the desired byproducts.
Robust Materials for Construction
Given the corrosive nature of the chemicals and the pollutants involved, the construction materials of NOx scrubbers are critical. Common materials include:
- Polypropylene (PP): Resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it a popular choice for scrubber construction.
- Polyethylene (PE): Known for its durability and chemical resistance.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): Offers good chemical resistance and is cost-effective.
- Teflon: Highly resistant to chemical corrosion, used in high-end scrubbers.
- Metals: Stainless steel and nickel alloys are used in high-temperature or highly corrosive environments due to their superior strength and durability.
Alternative Purification Methods
While wet scrubbers are highly effective, other NOx control methods are also used in various industrial settings:
- Adsorption: Activated carbon can adsorb NOx, although this method is generally less efficient for high-volume applications.
- Catalytic Reduction: Involves the use of catalysts to convert NOx into nitrogen and water. This method can achieve high efficiency but is often more expensive due to the cost of catalysts.
- Combustion Process Regulation: Adjusting the combustion process to reduce NOx formation at the source. This method is preventive but may require significant modifications to existing systems.
- Carbide Method: A less common method involving complex reactions with carbides to neutralize NOx.
Each method has its advantages and is selected based on specific industrial needs, regulatory requirements, and economic considerations.
Video: Overview Venturi Scrubber with a cyclonic separator
Final Thoughts About NOx Wet Scrubbers
Wet scrubbers are a crucial technology for controlling NOx emissions in industrial settings. Their effectiveness, combined with proper design and material selection, ensures compliance with environmental regulations and reduces the harmful impact of NOx on health and the environment. By understanding the operation, maintenance, and alternative methods, industries can make informed decisions to enhance their pollution control strategies.
For more detailed information and to explore specific NOx scrubber solutions, visit the original article here.